
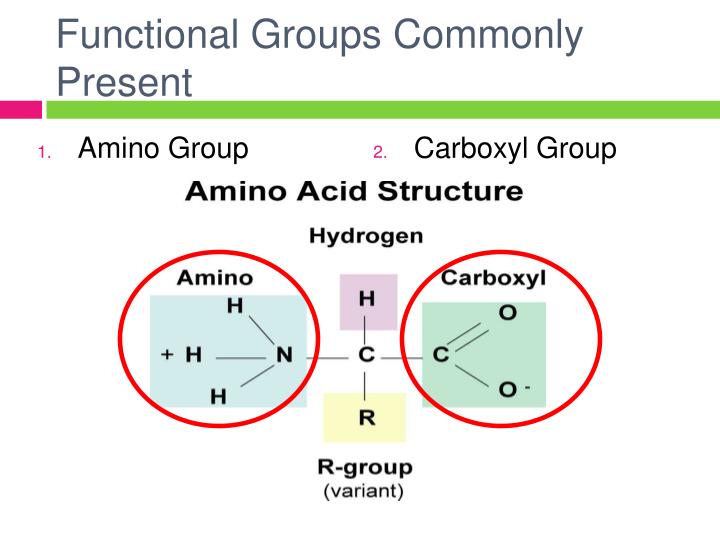
An example is the ninhydrin test in which the amine functional group of α-amino acids reacts with ninhydrin to form purple-colored compounds. Simple chemical tests that are used to detect amino acids take advantage of the reactivity of these functional groups. The reactivity of these functional groups is particularly important in linking amino acids together to form peptides and proteins, as you will see later in this chapter. Table 8.3 pIs of Some Representative Amino Acids Amino AcidĪmino acids undergo reactions characteristic of carboxylic acids and amines. The modification occurs after the amino acid has been assembled into a protein. In some cases an amino acid found in a protein is actually a derivative of one of the common 20 amino acids (one such derivative is hydroxyproline). Glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (Greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). It was obtained from protein found in asparagus juice (hence the name).

The first amino acid to be isolated was asparagine in 1806. The only amino acid whose R group has a pK a (6.0) near physiological pHĪlmost as strong a base as sodium hydroxide Tcarboxyl groups are ionized at physiological pH also known as aspartatĪrboxyl groups are ionized at physiological pH also known as glutamateĪmino acids with a positively charged R group Common Name Oxidation of two cysteine molecules yields cystineĪmino acids with a negatively charged R group Common Name Named for its similarity to the sugar threose Side chain functions as a methyl group donorĬontains a secondary amine group referred to as an α-imino acidĪmino acids with a polar but neutral R group Common Name The only amino acid lacking a chiral carbonĪn essential amino acid because most animals cannot synthesize branched-chain amino acidsĪlso classified as an aromatic amino acid Table 8.2 Common Amino Acids Found in Proteins Amino acids with a nonpolar R group Common Name We end the chapter with a discussion of enzymes-the proteins that act as catalysts in the body. We begin our study of proteins by looking at the properties and reactions of amino acids, which is followed by a discussion of how amino acids link covalently to form peptides and proteins. Immunoglobulins recognize and breakdown foreign molecules. Protect cells or the organism from foreign substances Ovalbumin stores amino acids in the egg white that will be used by the developing bird. Insulin regulates the activity of specific enzymes in the body. Regulate the functioning of other proteins
Hemoglobin transports oxygen from the lungs throughout the body.

Transport substances from one place to another Myosin is one protein needed for the contraction of muscles. Keratin is the primary protein of hair and wool. Α-Amylase catalyzes the hydrolysis of starch and glycogen. Table 8.1 Classification of Proteins by Biological Function Classification


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
